Your bright idea ...but please not flammable
Burning behavior
Most plastics are flammable by nature. To ensure that they can also be used in areas where flame protection is required, the use of flame retardants and the verification of their burning behavior by means of various fire tests have become established. Characteristic values in this area include, for example, burning speed (or burning rate), flammability (or ignitability), and the ability of a material to self-extinguish after contact with a flame.
In fire testing, it can make a difference whether a component section or specially manufactured test specimens are tested. We would be pleased to help you decide which procedure should be preferred with regard to your application.
The KUZ offers different fire tests in the accredited area of the testing laboratory:
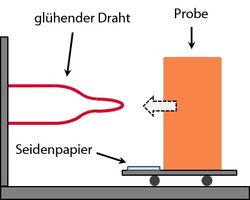
- Horizontal burning test (automotive applications)
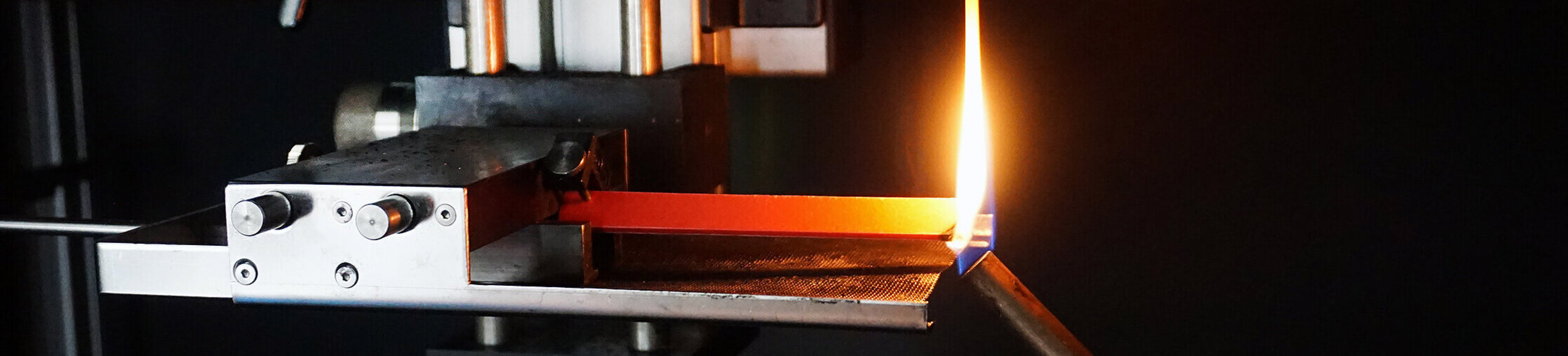
Part of the approval process for a component in a vehicle is testing its burning behavior. For use in the interior, it must be ensured that the materials used are either self-extinguishing or that the fire spreads only very slowly. For this purpose, the horizontal burning test is carried out in accordance with DIN 75200, ISO 3795 or FMVSS 302. Worldwide, there are several equivalents of this regulation, among others as country regulations or test specifications of various automotive companies. The technical equipment required and the procedure are comparable. Differences exist in the specimen geometry and the limit values to be complied with.
If the horizontal burning test cannot be carried out on the component because of its size, because of openings or because of a complicated shape, suitable test plates can be injection molded in the KUZ.
- Flammability of plastic parts according to UL94 (electronics & electrical engineering)
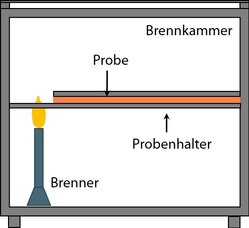
Originally developed for testing the flame retardancy of plastics in electrical equipment, the American UL 94 regulation is now the most common test for classifying the burning behavior of plastics. The German equivalent of the regulation is contained in the DIN EN 60695 series of standards. The best known are the vertical test (V-0, V-1, V-2) and the horizontal test (HB) according to UL 94. Specific tests are included in UL 94 for foams, films and other products.
In the UL 94 burning test, the specimen - in a vertical or horizontal position - is exposed to a flame and it is determined
- whether and when the specimen extinguishes after the flame is removed
- whether a burning drip occurs or
- how quickly the fire progresses (horizontal burning test) proceeds.
The vertical burning test is the tougher test, since the sample must extinguish itself within a short time in order to pass the test.
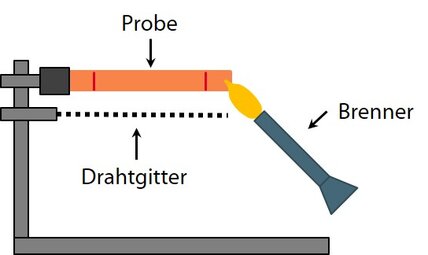
- Glow wire test (electronics & electrical engineering)
Glow wire tests according to DIN EN 60695-2-11/12/13 are used to assess the flammability or ignitability of materials or components in electronic equipment. These tests are intended to simulate how a plastic or component behaves when it comes into contact with overheated metallic parts. Consequently, a glowing conductor loop is brought into contact with the plastic surface. Based on the observations, a classification of the material or component according to the applicable test standard is derived.
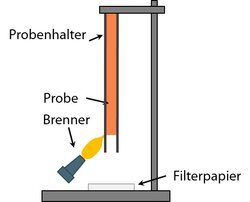
- Building materials: testing according to DIN EN ISO 11925 and DIN 53438
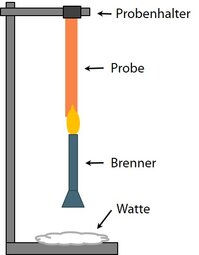
If plastics are used in construction, they have also to pass various tests to assess their fire behavior. This is to ensure that smoldering fires, which can spread quickly within building material composites, do not form in the finished building product. Based on the results of the various fire tests, the building materials are classified in the respective class according to DIN 4102 or DIN EN 13501-1.
Basic tests for assessing the burning behavior of building materials are the so-called single flame test according to DIN EN ISO 11925-2 and the edge or surface flame test according to DIN 53438. In both test methods, a vertically attached sample is exposed to a small flame from below. It is observed how quickly the flame spreads over the sample and whether it extinguishes again by itself.
Ourfire testing services in detail
Our equipment at a glance
Test facility BKF
Horizontal burn test
Dr.-Ing. Georg Wazau Meß+ Prüfsysteme GmbH
Burn test device according to UL 94
Dr.-Ing. Georg Wazau Meß+ Prüfsysteme GmbH
Test facility BBK
Vertical burning test building materials
Dr.-Ing. Georg Wazau Meß+ Prüfsysteme GmbH
GPG 3
Glow wire tester
Fischer Electronik












 "/>
"/>